As environmental awareness grows, the demand for sustainable roofing materials is also increasing. Homeowners and builders alike are seeking eco-friendly options that not only reduce environmental impact but also provide durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. This guide explores the various sustainable roofing materials available today, highlighting their benefits, drawbacks, and suitability for different climates and architectural styles.
Understanding Sustainable Roofing Materials
Sustainable roofing materials are those that are produced, used, and disposed of in ways that have minimal negative impact on the environment. This includes using renewable resources, minimizing waste and emissions during manufacturing, and ensuring the materials can be recycled or safely decomposed at the end of their lifecycle. Sustainable roofing not only contributes to environmental protection but can also offer cost savings over time through improved energy efficiency and longevity.
Popular Sustainable Roofing Materials
1. Metal Roofing
Benefits: Metal roofing is one of the most durable and long-lasting roofing options, often lasting 50 years or more. It is highly recyclable, with many metal roofs being made from recycled materials. Metal roofs are also energy efficient, reflecting solar heat and reducing cooling costs in hot climates. They are fire-resistant, low-maintenance, and can be installed over existing roofs, reducing waste.
Drawbacks: The initial cost of metal roofing can be higher than traditional asphalt shingles. Installation requires specialized skills, which can add to the cost. Additionally, metal roofs can be noisy during rain or hailstorms if not properly insulated.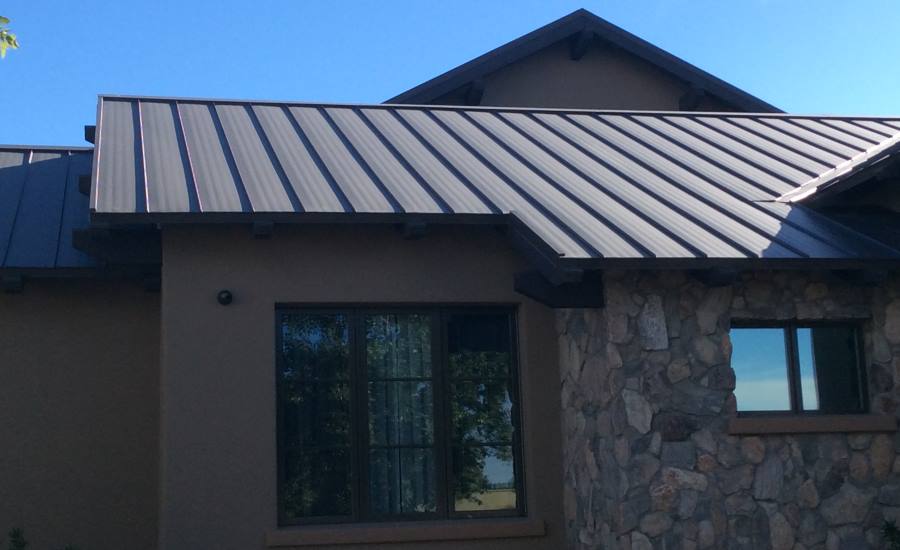
2. Recycled Shingles
Benefits: Recycled shingles are made from waste materials such as plastic, rubber, or wood fiber. These shingles divert waste from landfills and reduce the need for new raw materials. They are durable, often mimicking the look of traditional shingles, and are available in a variety of colors and styles. Recycled shingles can also be more affordable than other sustainable options.
Drawbacks: The lifespan of recycled shingles can vary, with some types not lasting as long as other roofing materials. They may also require more frequent maintenance. The environmental benefits can vary depending on the specific materials and manufacturing processes used.
3. Clay and Concrete Tiles
Benefits: Clay and concrete tiles are highly durable, often lasting 50 to 100 years. They are made from abundant natural materials and can be recycled at the end of their life. These tiles provide excellent thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy costs. They are also resistant to fire, rot, and insect damage.
Drawbacks: Clay and concrete tiles are heavy, requiring a strong roof structure for support. The installation process is labor-intensive and can be costly. In cold climates, freeze-thaw cycles can cause cracking in clay tiles, reducing their lifespan.
4. Slate Roofing
Benefits: Slate is a natural stone that is incredibly durable and can last over 100 years. It offers a unique, high-end aesthetic that is unmatched by other materials. Slate is fire-resistant, low-maintenance, and environmentally friendly, as it is a natural, recyclable material.
Drawbacks: Slate is one of the most expensive roofing materials both in terms of material cost and installation. It is also very heavy, requiring a reinforced roof structure. Slate can be brittle, making it susceptible to damage from heavy impacts.
5. Green Roofs
Benefits: Green roofs, or living roofs, consist of a waterproof membrane covered with soil and vegetation. They provide excellent insulation, reducing heating and cooling costs. Green roofs absorb rainwater, reducing runoff and the risk of flooding. They also improve air quality and provide habitats for wildlife in urban areas.
Drawbacks: Green roofs require significant structural support due to their weight. They also need regular maintenance to ensure the health of the plants and the integrity of the waterproof membrane. The initial installation cost can be high, though this is often offset by long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
6. Solar Shingles
Benefits: Solar shingles combine the functionality of roofing material with solar panels, allowing homeowners to generate electricity from their roof. This can significantly reduce or eliminate electricity bills and lower carbon footprints. Solar shingles are designed to blend in with traditional roofing materials, providing a seamless look.
Drawbacks: The initial cost of solar shingles is high, though tax incentives and energy savings can offset this over time. They require professional installation and may not be suitable for roofs with complex shapes or heavy shading.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Sustainable Roofing Materials
Climate Suitability
The local climate plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable roofing material. For example, metal roofs are excellent for hot climates due to their reflective properties, while green roofs provide insulation benefits in both hot and cold climates. Clay and concrete tiles are ideal for areas with a mild climate, as they can crack in extreme cold.
Cost
While sustainable roofing materials can have a higher upfront cost, they often provide long-term savings through durability, low maintenance, and energy efficiency. It’s important to consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and potential energy savings.
Aesthetic Appeal
The visual appeal of the roofing material can enhance the overall look of the home. Slate and clay tiles offer a classic, high-end appearance, while metal and recycled shingles provide more contemporary options. Green roofs add a unique, natural element to the architecture.
Local Building Codes and Regulations
Before choosing a roofing material, it’s important to check local building codes and regulations. Some areas may have restrictions on certain materials due to weight, fire resistance, or other factors. Additionally, some regions offer incentives or rebates for using sustainable materials, which can help offset costs.
Environmental Impact
Consider the entire lifecycle of the roofing material, from production to disposal. Materials like metal and slate have lower environmental impacts due to their recyclability and longevity. Recycled shingles and green roofs help reduce waste and improve sustainability.
Conclusion
Choosing the right sustainable roofing material requires careful consideration of various factors, including climate suitability, cost, aesthetic appeal, and environmental impact. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each option, homeowners can make informed decisions that contribute to both the longevity of their homes and the health of the planet.
Sustainable roofing is not just a trend but a crucial step towards reducing our environmental footprint and creating more energy-efficient homes. Whether opting for the durability of metal, the natural beauty of slate, or the eco-friendly appeal of green roofs, there is a sustainable roofing material to suit every need and preference. As technology and manufacturing processes continue to advance, the range of eco-friendly roofing options will only expand, offering even more opportunities to build and renovate with sustainability in mind.